We are taking
climate action
Since April 17, 2023, we have purchased
88,200
kg of carbon credits
Spread the Word
That’s the same climate impact as:

1,458
new trees planted

19.6
cars off the road for a year

11.1
homes’ annual energy usage

233
flights from LA to New York
* calculations based on U.S. EPA and ICAO formulas
59.3%
Technology-based Reductions
Our approach
We partner with CNaught to purchase a diversified portfolio of high-quality carbon credits that is designed to maximize impact, mitigate risk, and foster innovation. A portfolio approach to carbon credits is recommended by the World Economic Forum, and the CNaught portfolio embodies the science-based best practices laid out in Oxford’s Principles for Carbon Offsetting.
Select a category to learn more about it
Technology-based Reductions
This category covers a wide range of projects that aim to reduce and avoid emissions versus business as usual. Examples include: natural gas leak repairs, destruction of refrigerants that would otherwise be vented to the atmosphere, and capture of methane emitted from landfills.
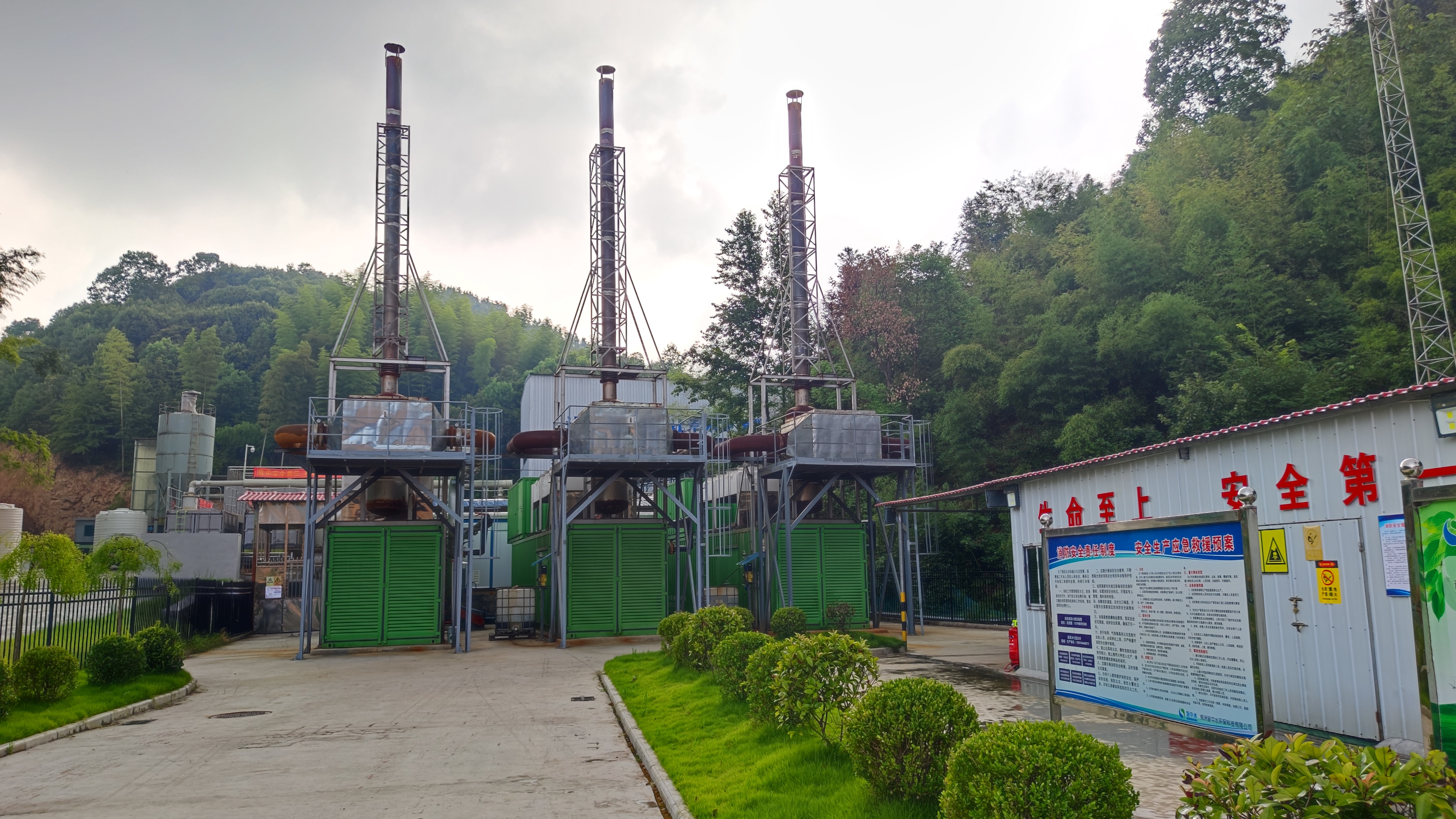

Liling Landfill Gas Project
This project collects landfill gas to generate 3.2MW of electricity at a landfill in Hunan Province, China, avoiding the emission of methane (a potent greenhouse gas) into the atmosphere and using the methane to generate power and displace dirtier coal-fired power in the electric grid.
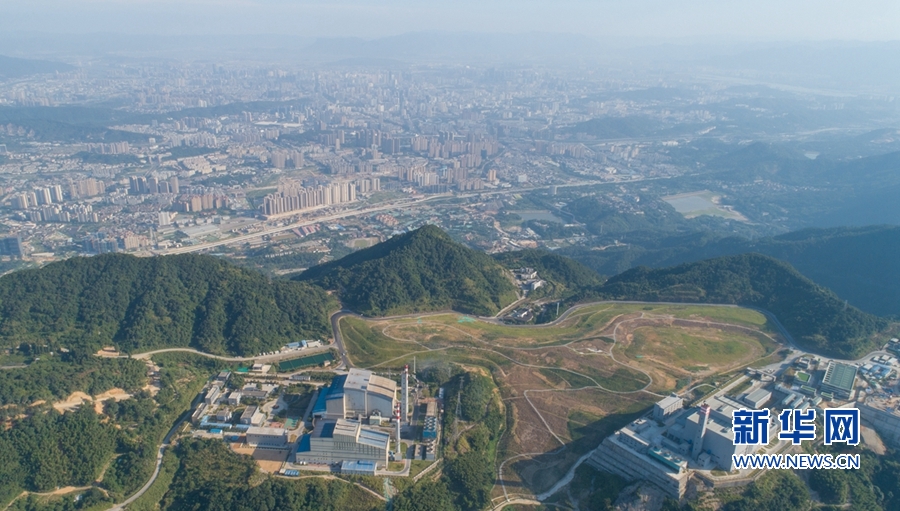

Fuzhou Hongmiaoling Landfill Gas to Electricity
This project collects landfill gas to generate 2.5MW of electricity at a landfill in southeastern China, avoiding the emission of methane (a potent greenhouse gas) into the atmosphere and using the methane to generate power and displace dirtier coal-fired power in the electric grid.
Nature-based Reductions
This category typically consists of nature-based projects that help retain an existing source of natural carbon storage that would otherwise be at risk — for example, rainforests that would be cut down for development or peat bogs that might be drained for agriculture.

Katingan Mentaya Conservation
One of the highest-regarded avoided deforestation projects in the world, this project protects and restores 149,800 hectares of peatland ecosystems in Indonesia that would likely otherwise have been converted to palm and other plantations.
Nature-based Removals
This category typically consists of nature-based projects that remove existing carbon and store it in new plants, trees, or soil — for example, planting trees in an area that has previously been clear cut or restoring plant life to tidal wetlands.

TIST Program in Uganda
One of the oldest and most successful reforestation projects ever undertaken, TIST partners with thousands of small landowners and subsistence farmers in Uganda to plant a mixture of native trees, food bearing trees, and commercial trees in areas that have been substantially deforested.

X-Hazil
An Improved Forest Management project that combines regeneration practices, reforestation efforts, and silvicultural treatments to enhance forest sustainability and ecosystem integrity, all monitored under FSC guidelines.
Technology-based Removals
This is a highly diverse category of projects that includes cutting-edge engineered solutions that hold significant promise but are not yet available at scale. Examples include direct air capture technology and storage of carbon through enhanced rock weathering.

Charm Industrial Bio Oil
Charm collects waste from plants that have captured carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, applies a heating process called pyrolysis that converts the plant waste into bio-oil, and injects that bio oil into deep wells or caverns where it hardens and will be stored permanently instead of being released to the atmosphere as the plants decay.